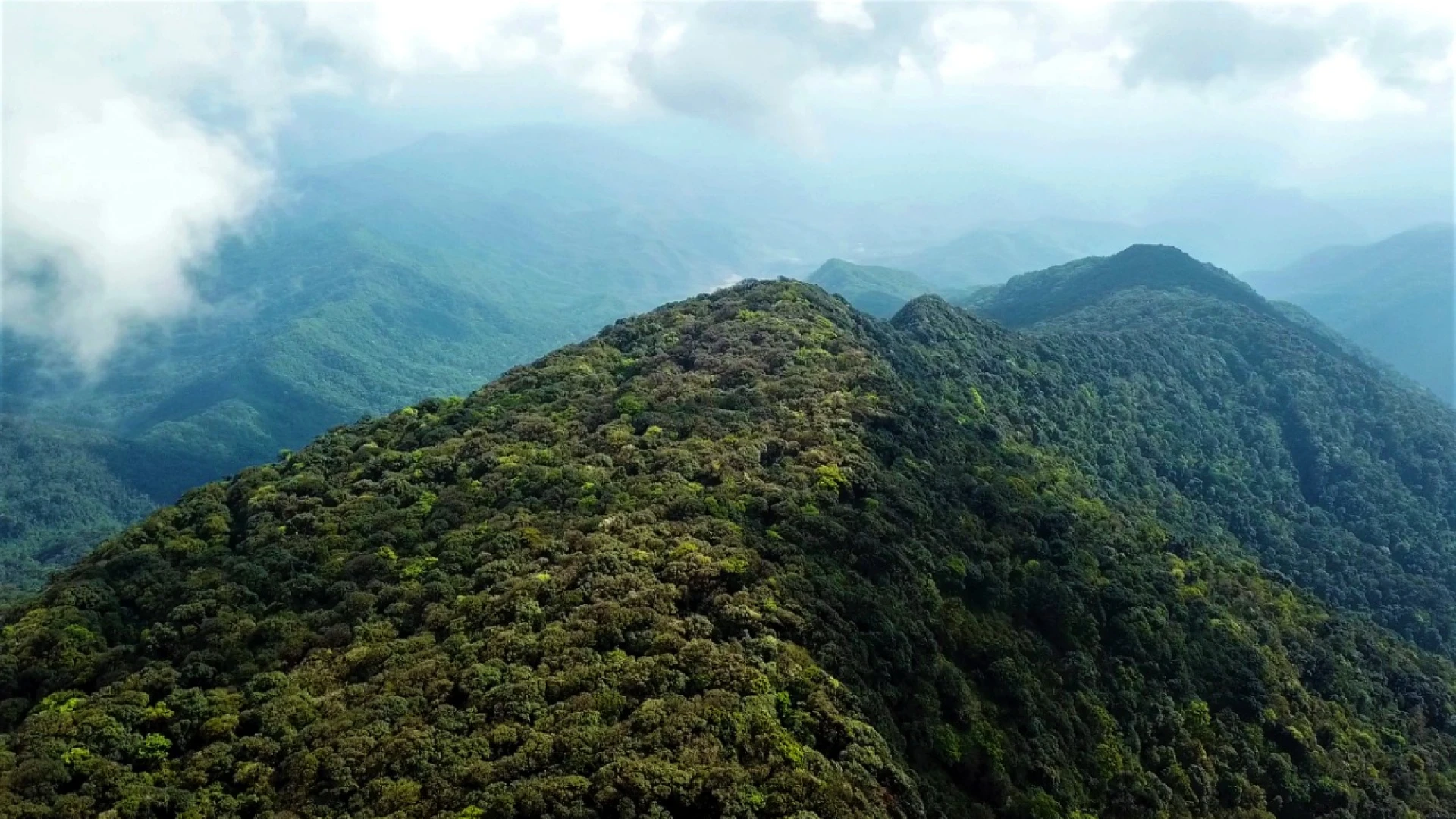
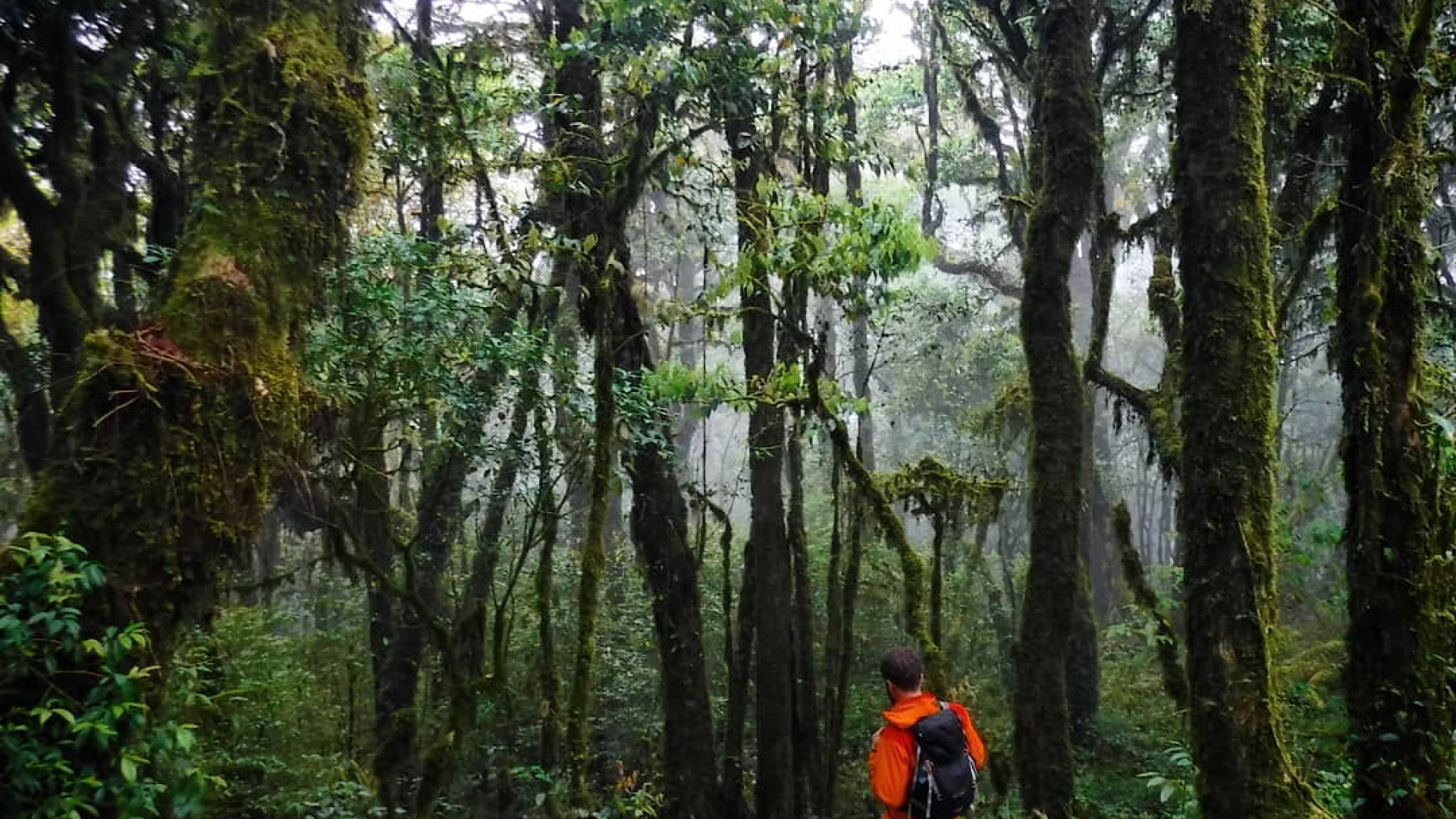
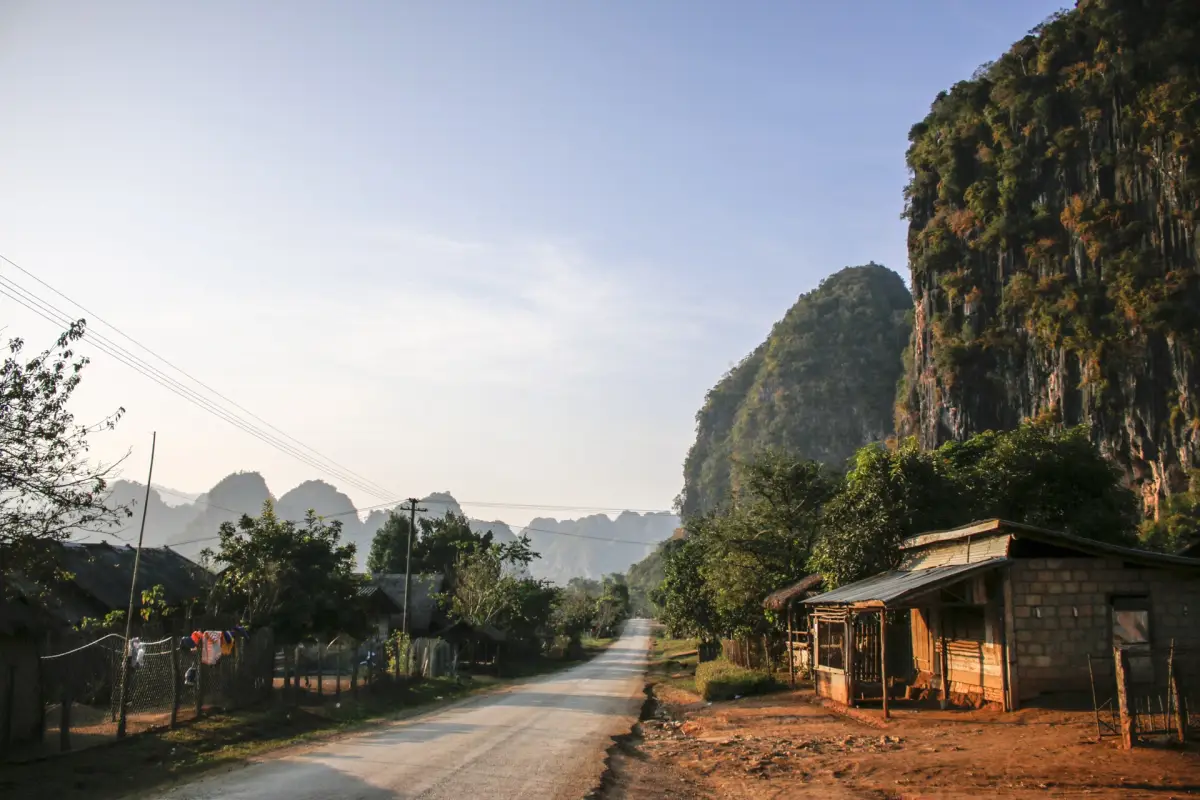
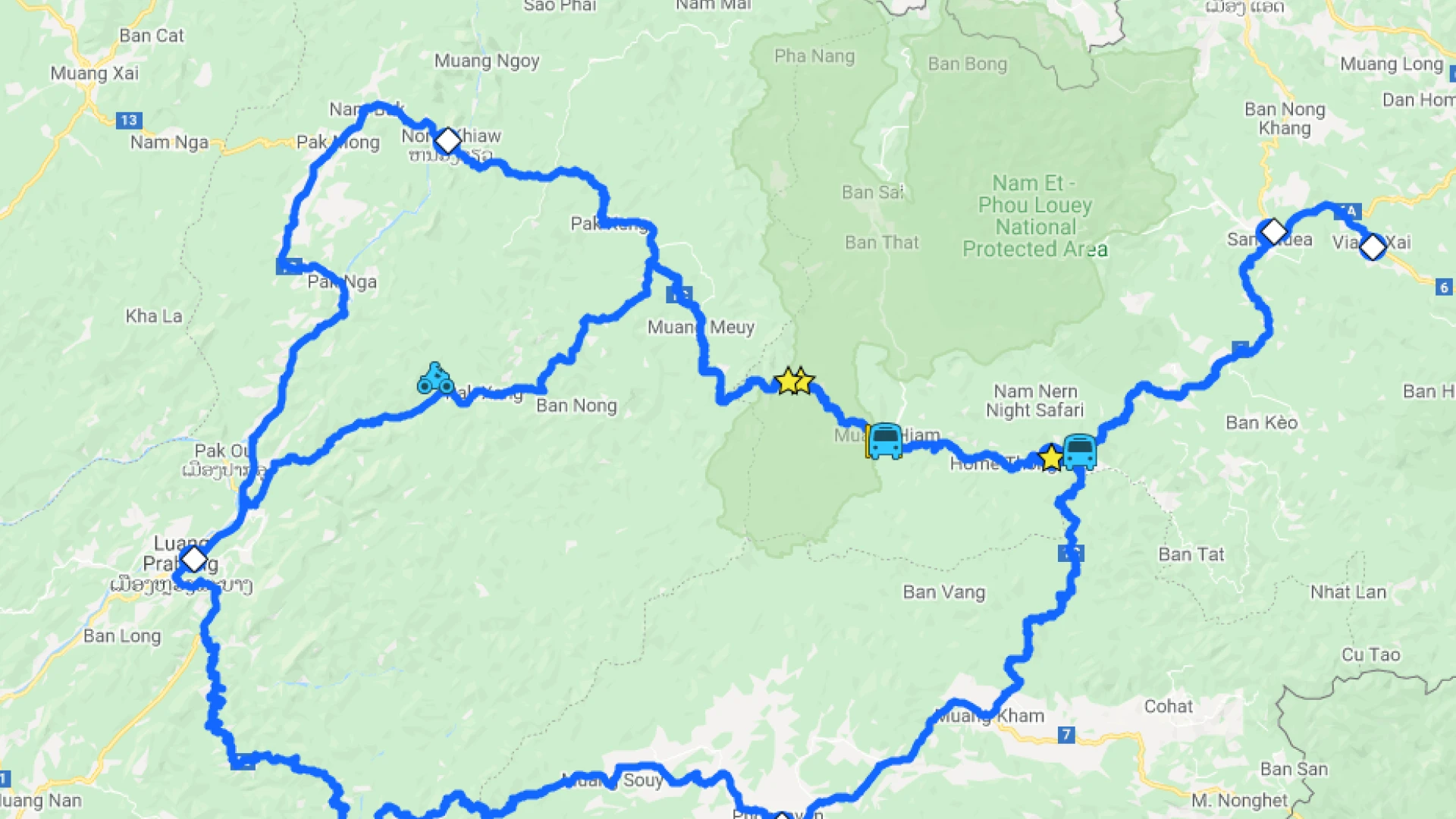
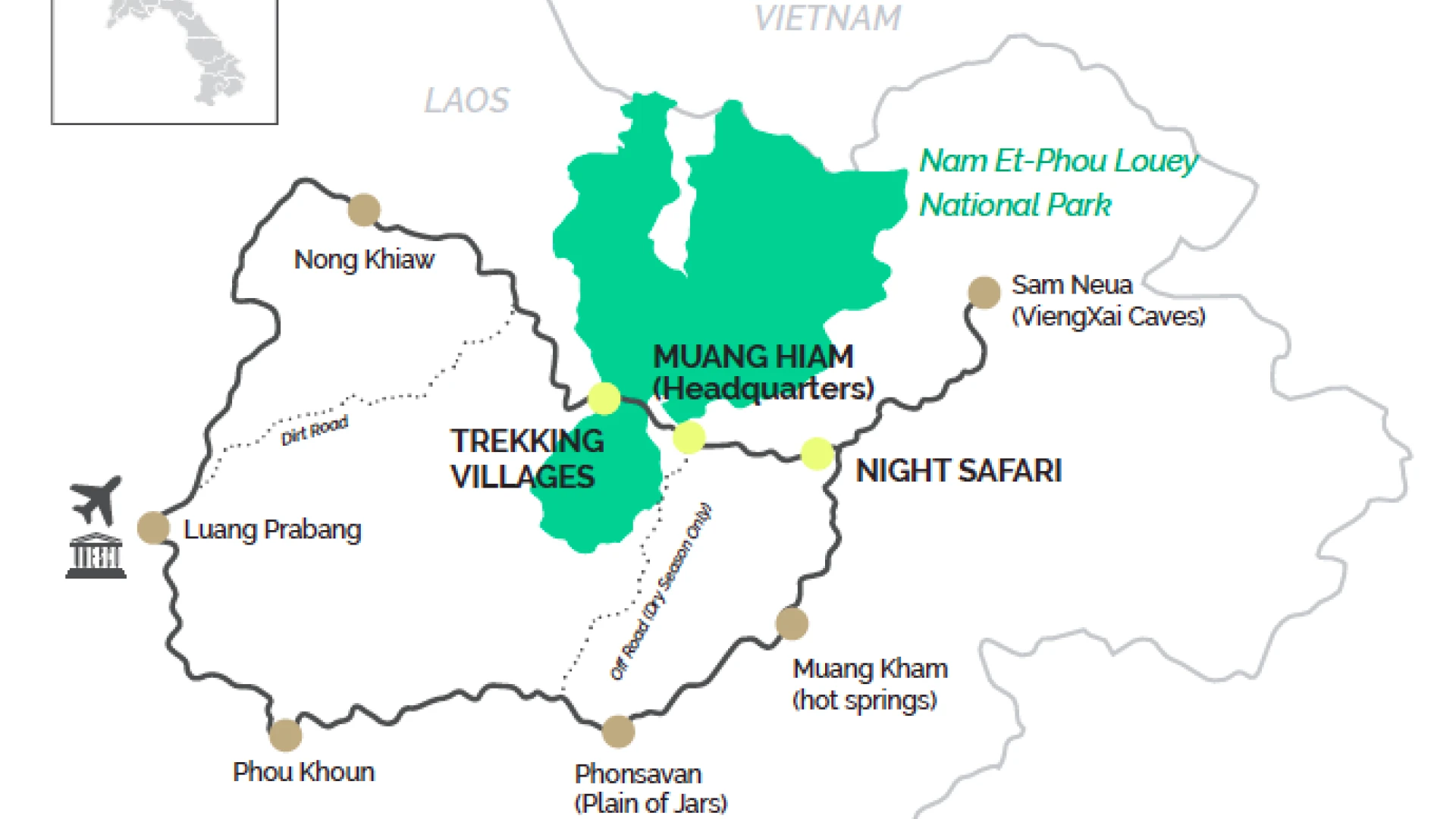
Nam Et–Phou Louey (pronounced “naam et poo loo-ee”) National Protected Area (NPA) is located in the north-east of Lao PDR. With an area of 410,720 ha, it is the largest of Laos’ NPAs, covering seven districts and three provinces (Houaphan, Luang Prabang and Xieng Khouang provinces). Mostly hilly or mountainous, it is the source of many rivers. It is named after its two main features, the Nern and Et Rivers and Phou Louey Mountain (“Forever Mountain”). The area has primary forest remaining in many areas, a high level of biodiversity, and a number of endangered species including tiger, gaur, Sambar deer, and white-cheeked gibbon. Ecotourism activities at Nam Et-Phou Louey (NEPL) National Protected Area (NPA) have been developed to provide an additional livelihood opportunity for local people surrounding the Protected Area. All tours have been designed to create a direct link between conservation and tourism so that the money that visitors pay has a positive impact on encouraging local people to protect endangered wildlife. This is achieved through active community involvement, and the creation of conservation linked financial incentive mechanisms.
Topography
Nam Et-Phou Louey NPA is located between latitudes of 19.85-20.05 degrees N and longitudes 103.20-103.85 degrees E. The terrain is mountainous with altitude ranging between 336 and 2257 metres above sea level. The highest point is the peak of Phou Louey and the lowest the Nam Et river valley. The topography of the area is steep and the land suitable for agriculture is limited. Being such a mountainous area, the park is the source of many major rivers including Nam Nern, Nam Khan, Nam Et, Nam Seuang, and Nam Seng. In addition, there are many tributaries, which contribute significantly to the livelihoods of local people. The main importance of rivers to villagers relate to transportation, fishing, household water supply and irrigation amongst others.
Climate & Vegetation
Nam Et-Phou Louey NPA generally has a high upland climate with two seasons, dry and rainy. The rainy season runs between April and September and the dry season between October and March. The park is an important habitat for many wild species endemics to Indochina. However, only 0.1% of the NPA is undisturbed primary forest and 23.2% is partially disturbed/open forest, indicating long-standing encroachment.
Wildlife
There are five key species at NEPL, each representing the overall health of the ecosystem: the tiger, gaur, white-cheeked crested gibbon, Sambar deer, and otters. Nam Et-Phou Louey displays an outstanding diversity of carnivores, that includes six cat species (tigers, leopard, clouded leopard, Asian golden cat, marbled cat and leopard cat), dhole (status: vulnerable), two species of bear (Asian black bear and sun bear, status: vulnerable), and 11 small carnivores including civets, mustelids, and mongoose. A small elephant population persists along the Nam Et River. In 1998, over 40 species of bats were recorded at NEPL, of which three were new to Laos.
Conservation
Protecting Nam Et-Phou Louey’s rich biodiversity is a full-time task. There are five departments dedicated to conserving the area’s wildlife and forests: enforcement, conservation outreach, monitoring and research, land-use management, and ecotourism. The Nam Nern Night Safari is part of this ecotourism program: a village-development fund is funded by sightings of wildlife by visitors.
People of the Park
The livelihoods of the villagers in the area are very much associated with the natural environment by way of agricultural production and shifting cultivation. There are few sources of alternative employment and settlement are highly scattered and often in remote and inaccessible areas. A small number of villages also manufacture handicrafts and have simple services. According to the 2001 Poverty Assessment, the three main districts in Nam Et-Phou Louey, Houameuang, Viengkham, and Viengthong, fall into the second highest poverty bracket with poor villages making up more than 90% of the total (the poorest districts have 100% poor villages).
Visit
Currently the only way to visit Nam Et-Phou Louey is by doing the protected area’s wildlife ecotours: Nam Nern Night Safari or Trekking Tours. Ecotourism activities at Nam Et-Phou Louey (NEPL) National Protected Area (NPA) have been developed to provide an additional livelihood opportunity for local people surrounding the Protected Area. All tours have been designed to create a direct link between conservation and tourism so that the money that visitors pay has a positive impact on encouraging local people to protect endangered wildlife.